File formats
jpg - gif - bmp - png
Four file formats were used to investigate the relative merits of each format for use in web pages.
All formats were compressed.
jpg comments
The jpg file format is a lossy compression method that can be adjusted for quality. Better quality settings produce larger file sizes. The examples below illustrate quality levels of 0 and 7. At quality=0, blocking is evident and fine detail is smeared out. For this file, raising the quality setting produces a better image until at quality=7 no further improvement is noticed. However, even at quality=7, details in the water spray are lost in the compression artifacts.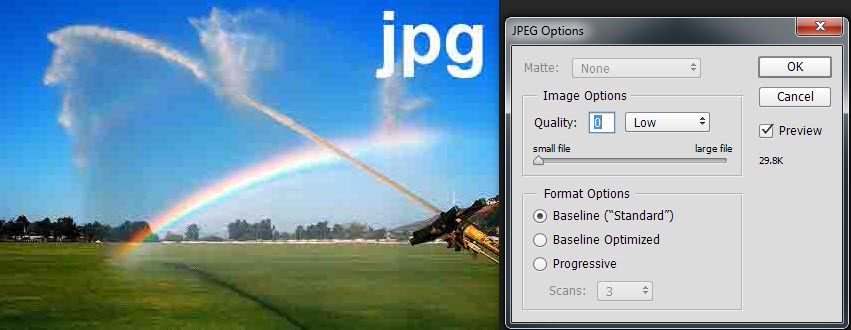
jpg at quality=0
file size=69KB
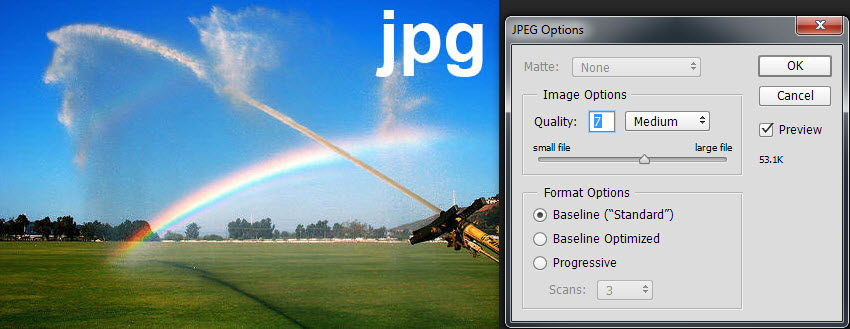
jpg at quality=7
file size=81KB
gif comments
The gif file format is a lossy compression method that gains much of its effect by supporting only 256 colors produced from a lookup table with an 8-bit index. Without further adjustments, gif images exhibit severe color banding in gradients. However, images are improved with dithering to help smooth transitions in the gradient.
gif with 256 colors and diffusion dither
file size=88KB
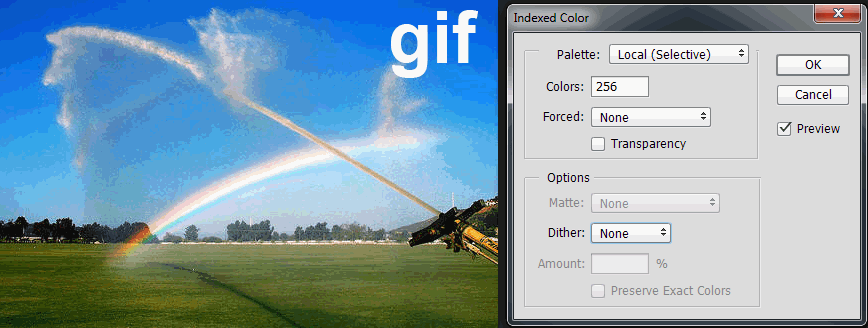
gif with 256 colors and no dither
file size=65KB
bmp comments
The bmp file format is a (generally) uncompressed file format that implements the Microsoft device-independent methodology. The format supports a range of color depths that depending on the image type can affect image quality in addition to file size.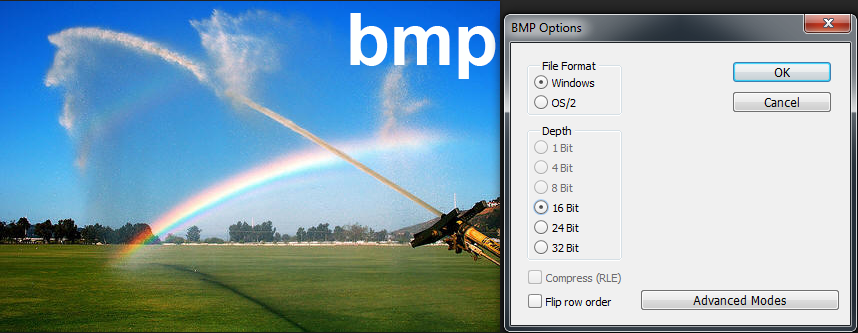
bmp with 16-bit color depth
file size=838KB
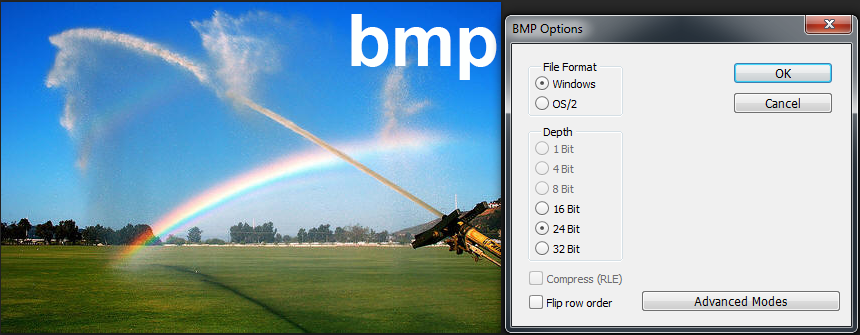
Bmp with 24-bit color depth exhibits marginal improvement in sky gradient.
Greater differences can be seen when the original sources files are higher quality that what was used in these examples.
file size=845KB
png comments
The png file format is a lossless file format that implements the Microsoft device-independent methodology.The format supports a range of color depths that depending on the image type can affect image quality in addition to file size.
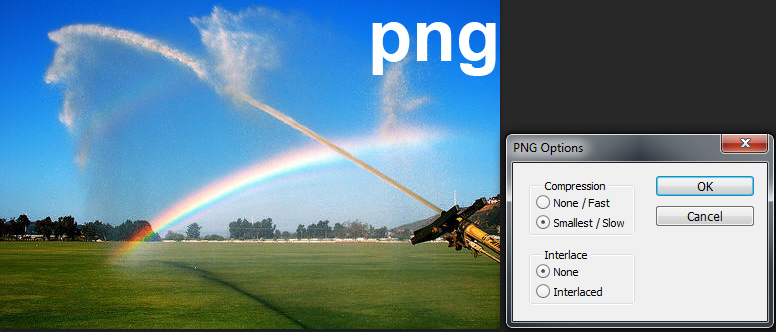
png files generally deliver excellent quality.
file size=274KB
Cropped and reduced image

cropped rainbow
file size=17KB
File format questions
Detailed descriptions of the file formats are provided in the comments and examples above. The last question of "State which is the best image format for displaying the image on the Internet and explain why" is best addressed by understanding that the concept of "best" is subjective. If such a thing as "best for the Internet" existed, then we would only have one format. Different formats exist because of different qualities that provide an advantage in certain applications. A short answer to the question is "it depends on your objectives and image type". A more expansive answer would suggest that one's format choice can be based on finding an appropriate balance between the needs of your application and the properties of each file format. Quality considerations argue for lossless formats while space or speed considerations argue for small files produced by lossy formats. And finally, alpha channel support is another important issue in the consideration of a file format. If you need text to float over background elements, then gif will not be your friend. If you don't want to study the details, then choose PNG. It is a pretty safe choice for most situations.A summary of these experiments would conclude:
1) uncompressed files are always larger than compressed
2) compression parameters that improve quality will also increase file size (like dithering)
3) color indexed files look pretty bad when used with continuous tone images
4) image pixel dimensions have a huge effect on file size and finally
5) some file fomats will perform well on certain types of images and poorly on other types (e.g. photos or graphics)
Word document question
The letter on the right has higer perceived edge sharpness after zooming in because it is a vector-based type face. The letter on the left is a bitmapped image. When the image is scaled, the typeface edges are recalculated and antialised down the the pixel level available on the current screen hardware. The bitmap is simply scaled from the original pixel dimensions and this results in a jagged edge.
Return to Assignment 3 page